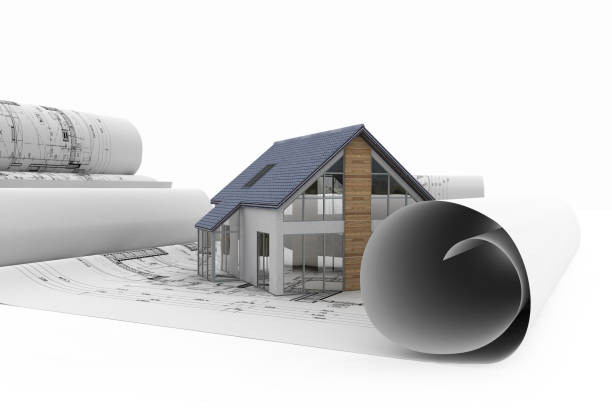
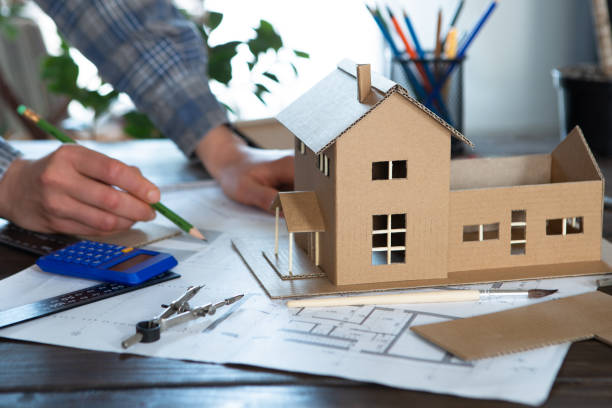
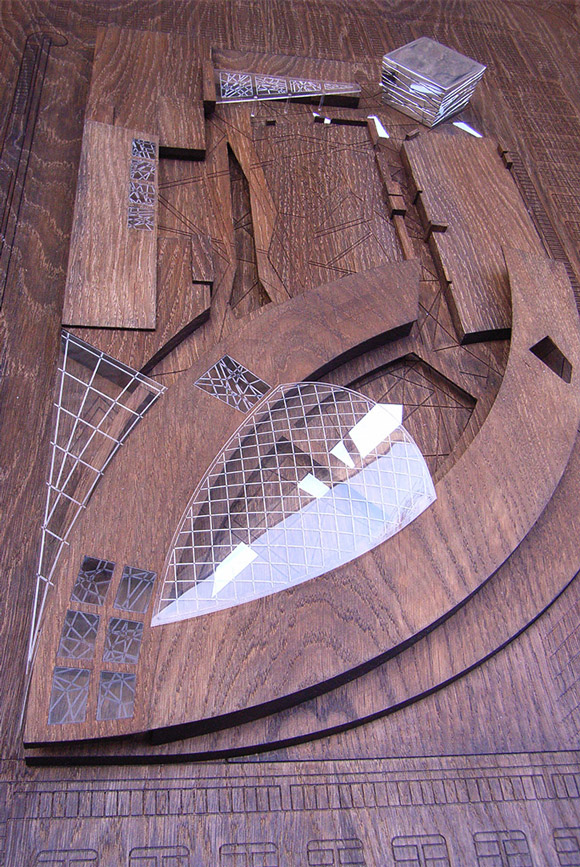
Technology and Processes involved in Architectural Model Making
The technology and processes involved in architectural model making have evolved significantly over the years, with advancements in digital tools and fabrication techniques. Here are some of the key technologies and processes used in architectural model making:
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Software: CAD software, such as AutoCAD, Rhino, SketchUp, and Revit, enables architects and model makers to create accurate digital representations of their designs. These tools allow for precise measurements and adjustments, making it easier to refine and perfect the design before creating a physical or digital model.

3D Modeling Software: Software like 3ds Max, Blender, and Rhino help create detailed and complex digital 3D models of architectural designs. These models can be used for design development, virtual walkthroughs, and creating realistic visualizations.
Rendering Software: To create realistic and immersive visualizations of architectural models, rendering software like V-Ray, Lumion, and Enscape is used. These tools take digital 3D models and apply materials, lighting, and environmental effects to generate high-quality images or videos that showcase the design.
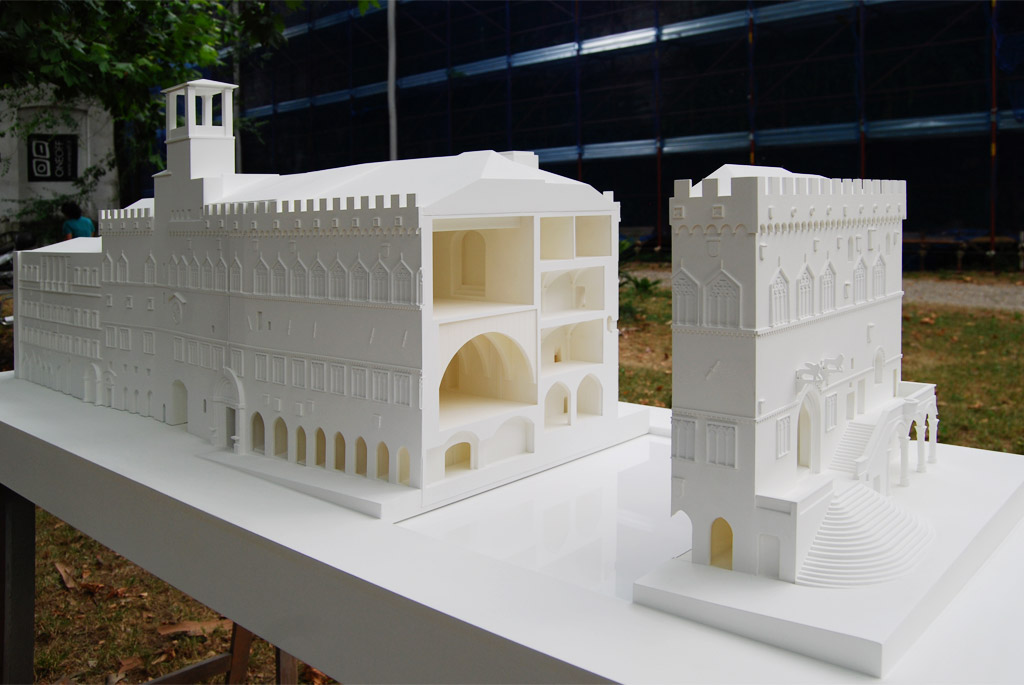
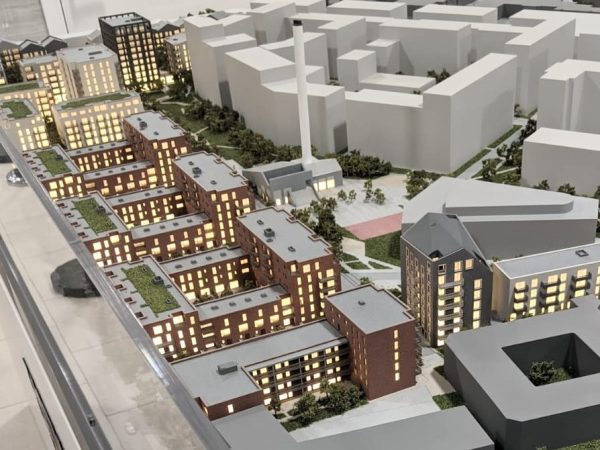
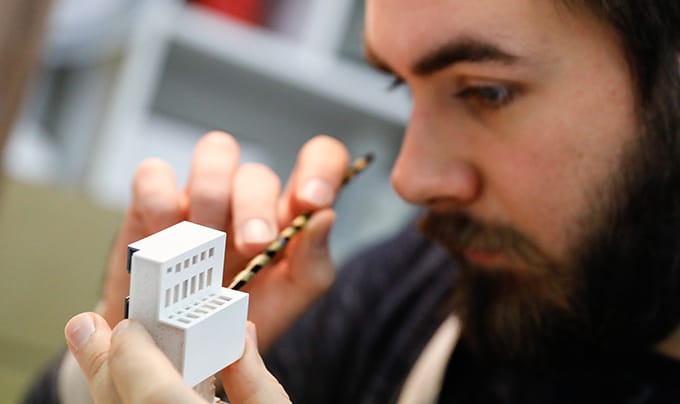
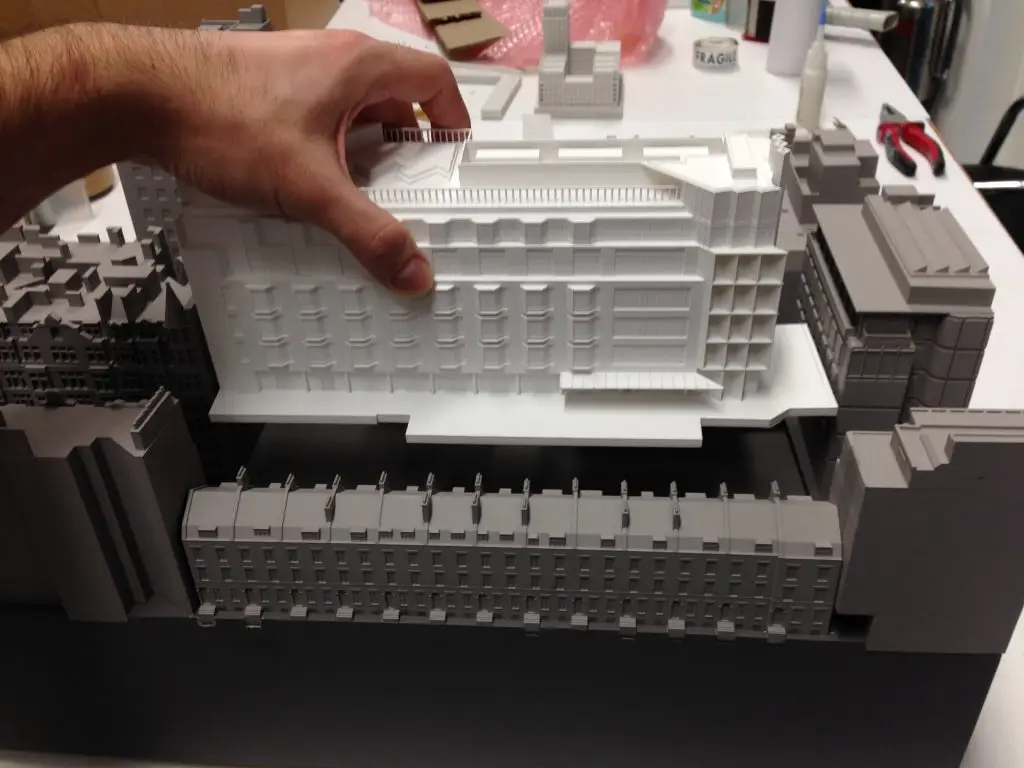
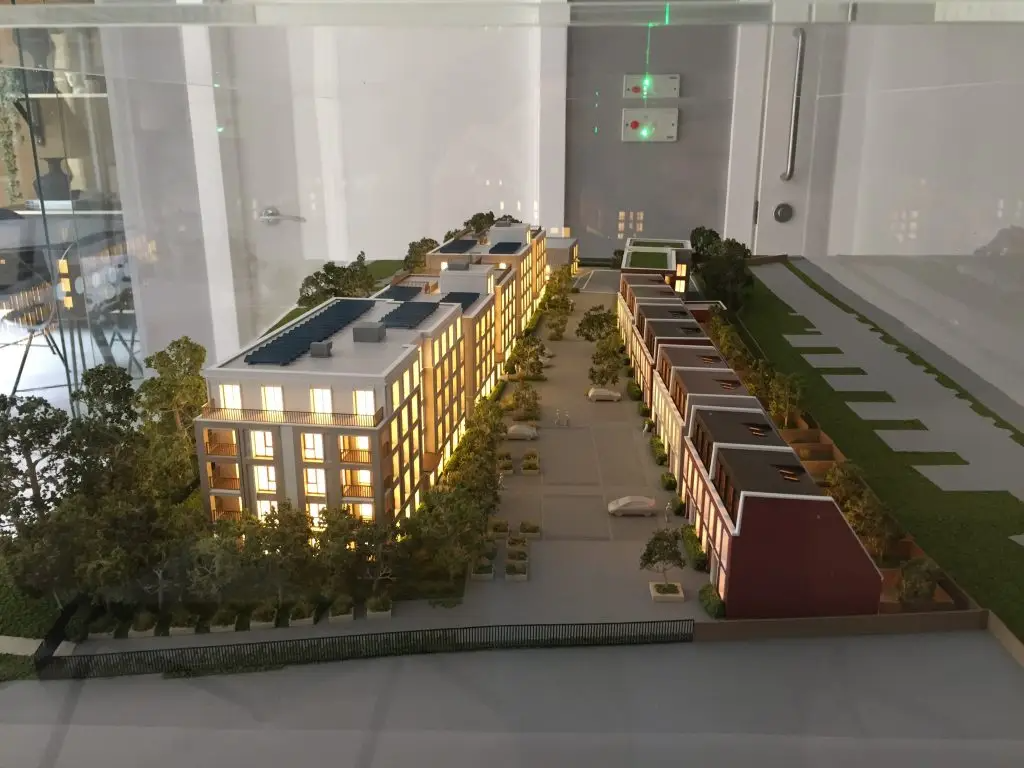
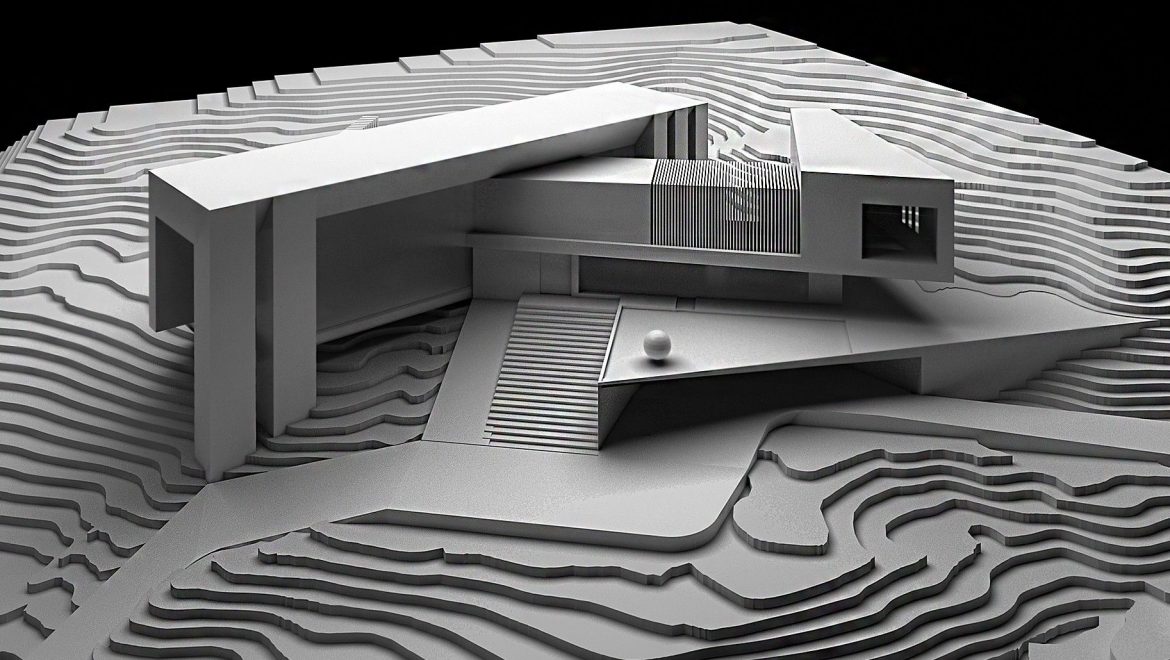
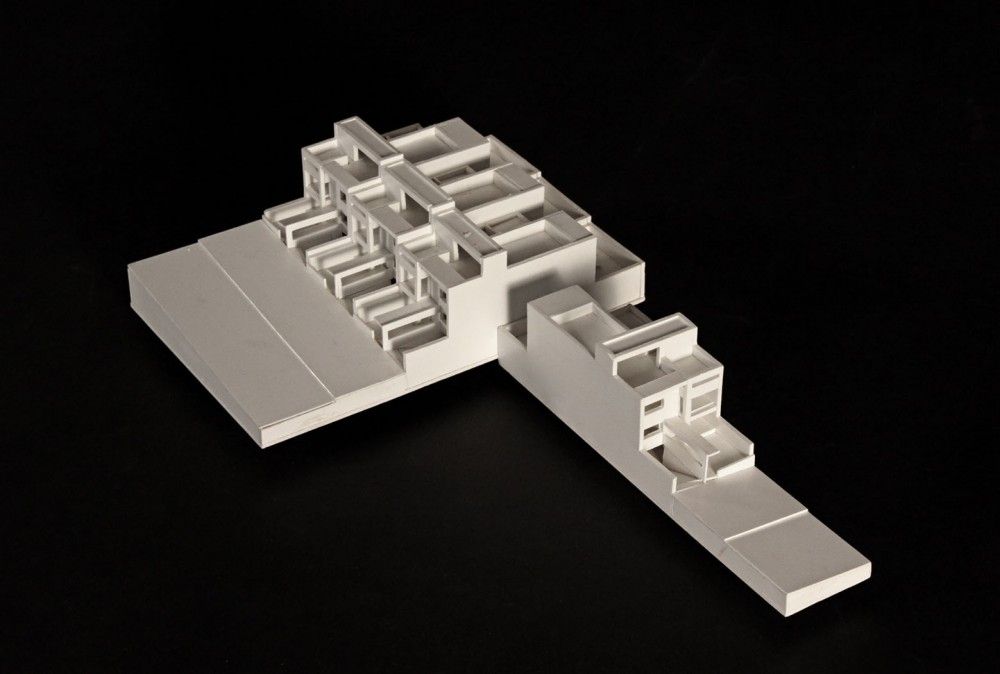
3D Printing: Additive manufacturing technologies, such as 3D printing, have revolutionized architectural model making. With a variety of materials available, including plastics, resins, and metals, 3D printing allows for the creation of highly detailed and intricate models, which can be used for design development or presentation purposes.

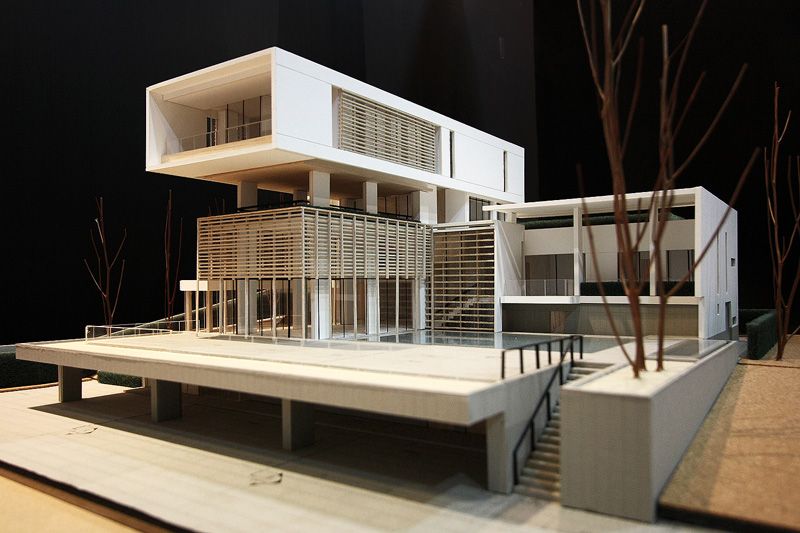
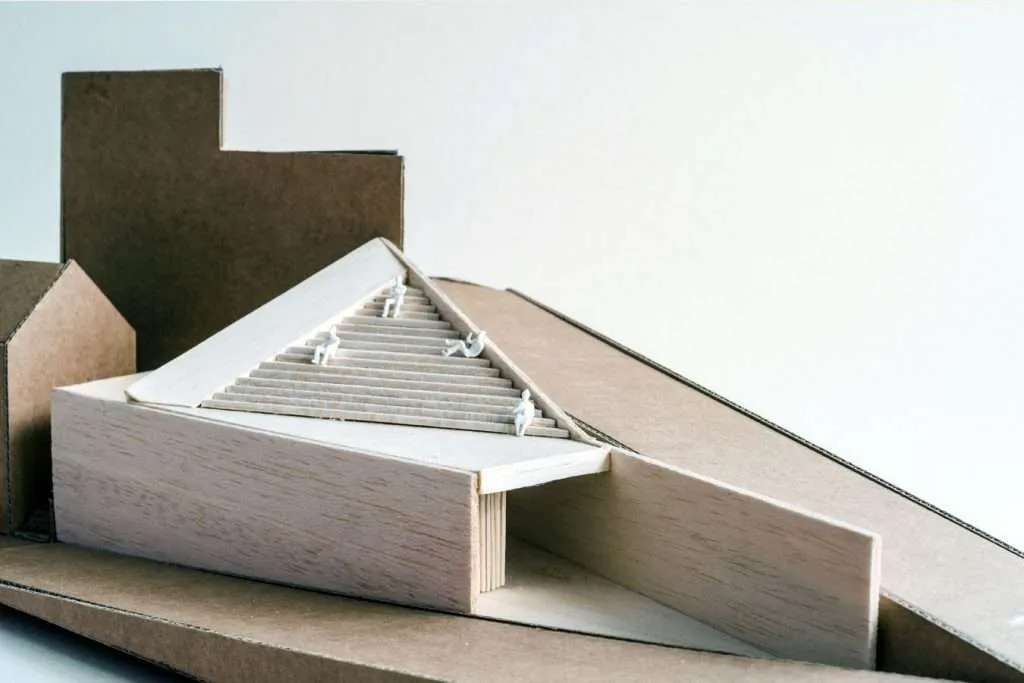
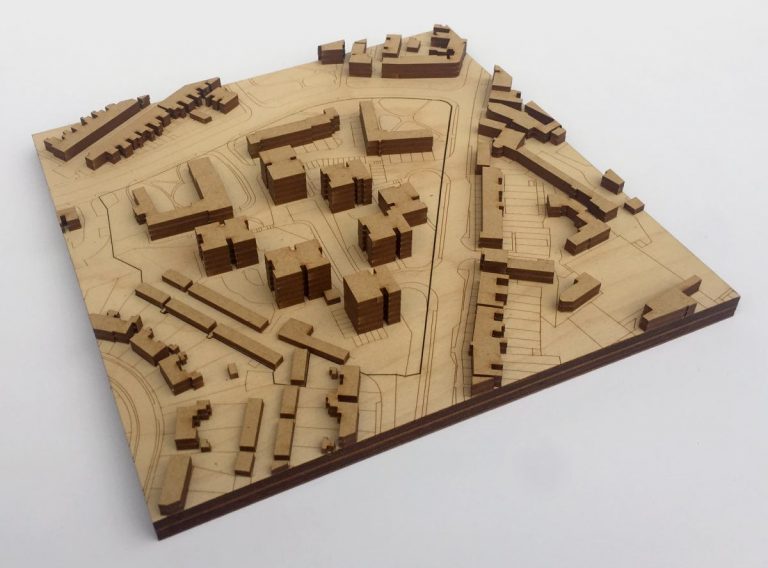
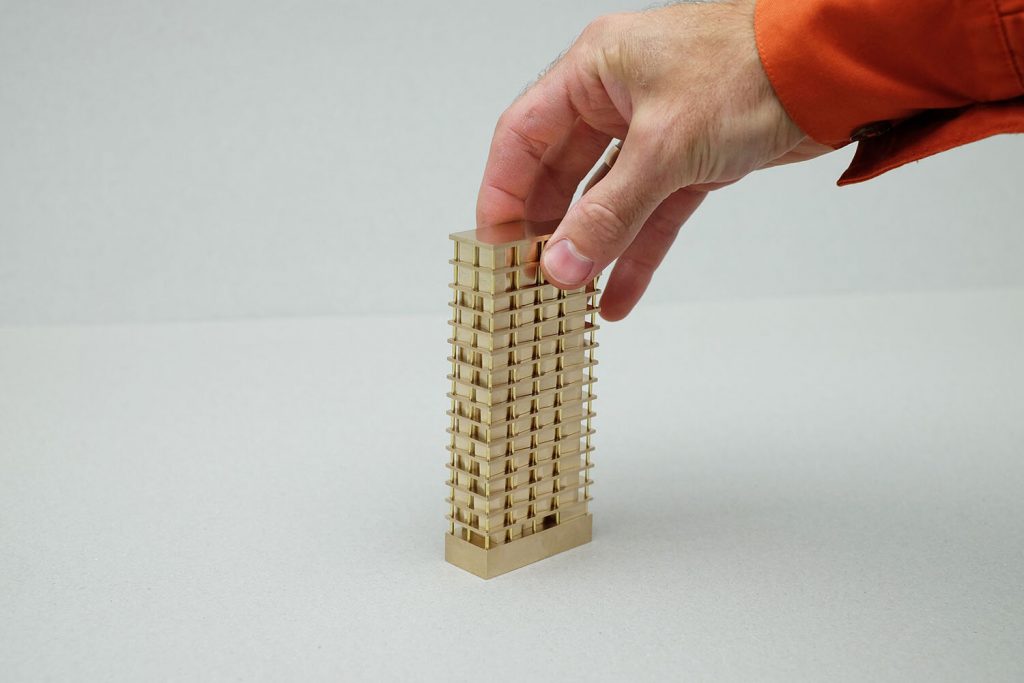
Laser Cutting and CNC Milling: Laser cutting and CNC milling machines provide a high level of precision and accuracy when cutting and shaping materials like wood, acrylic, and metal. These technologies have made it easier to create complex and detailed physical models.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR and AR technologies offer immersive ways to experience architectural designs. Architects and model makers can use VR headsets or AR apps to provide clients and stakeholders with a virtual walkthrough of their design, making it easier to visualize the completed project.
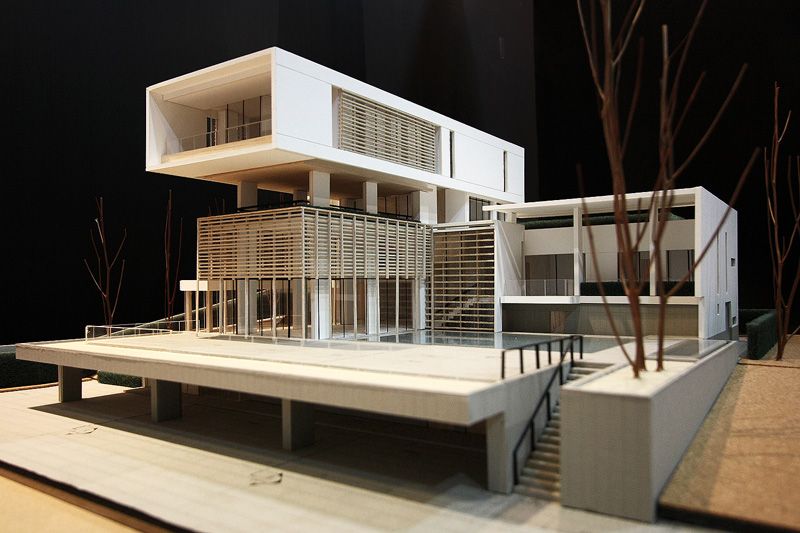
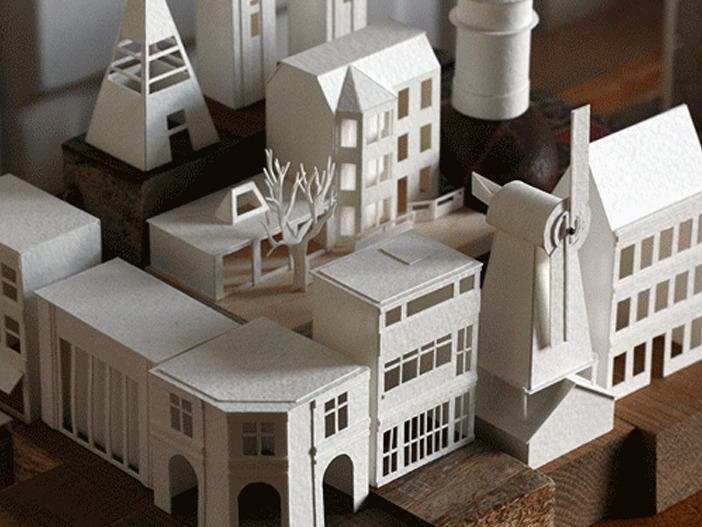
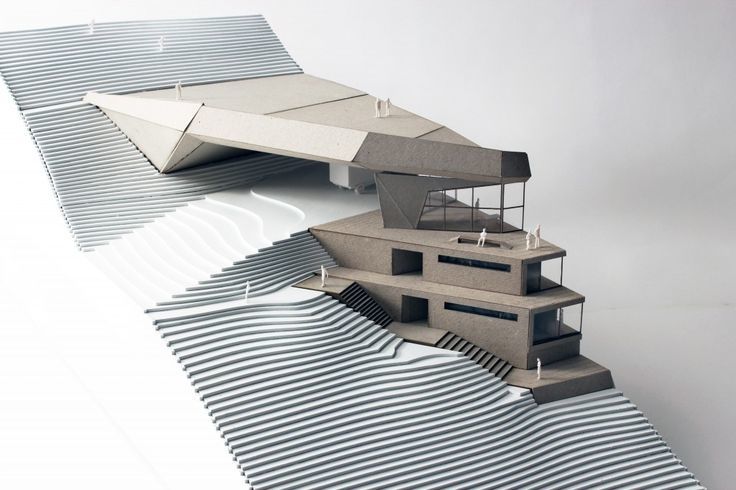
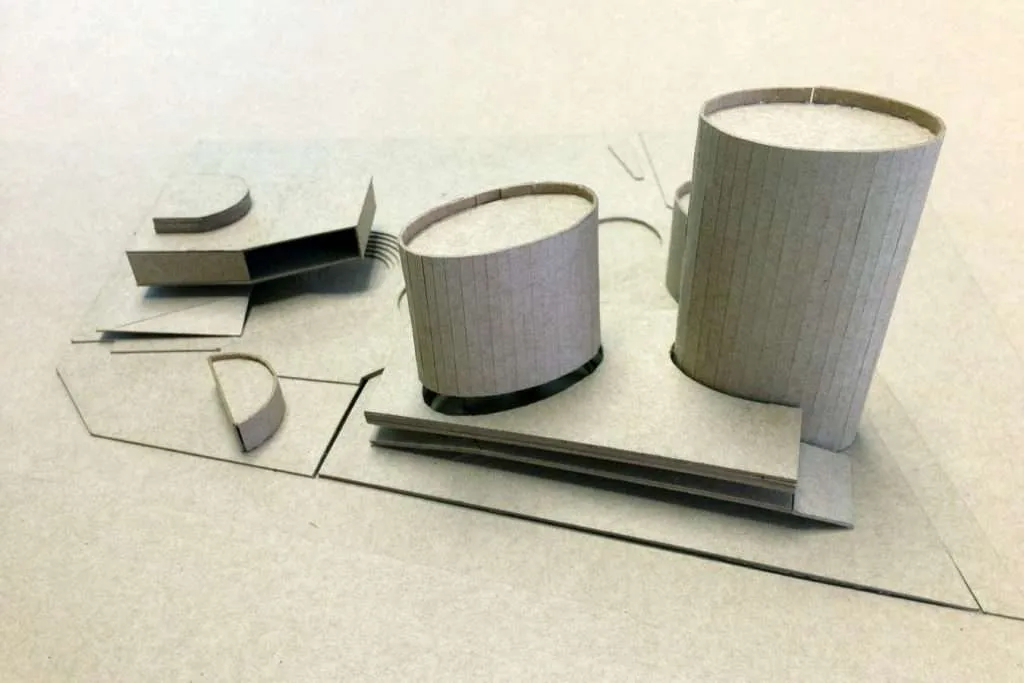
Traditional Model Making Techniques: Despite the advancements in digital tools and fabrication methods, traditional model making techniques, such as hand cutting, gluing, and painting, are still essential skills for many architectural model makers. These techniques are often employed in the early stages of design development or when creating concept models.
The combination of these technologies and processes allows architectural model makers to create highly detailed, accurate, and visually impressive models that aid in design development and communication. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that we will see even more sophisticated tools and techniques emerge in the field of architectural model making.