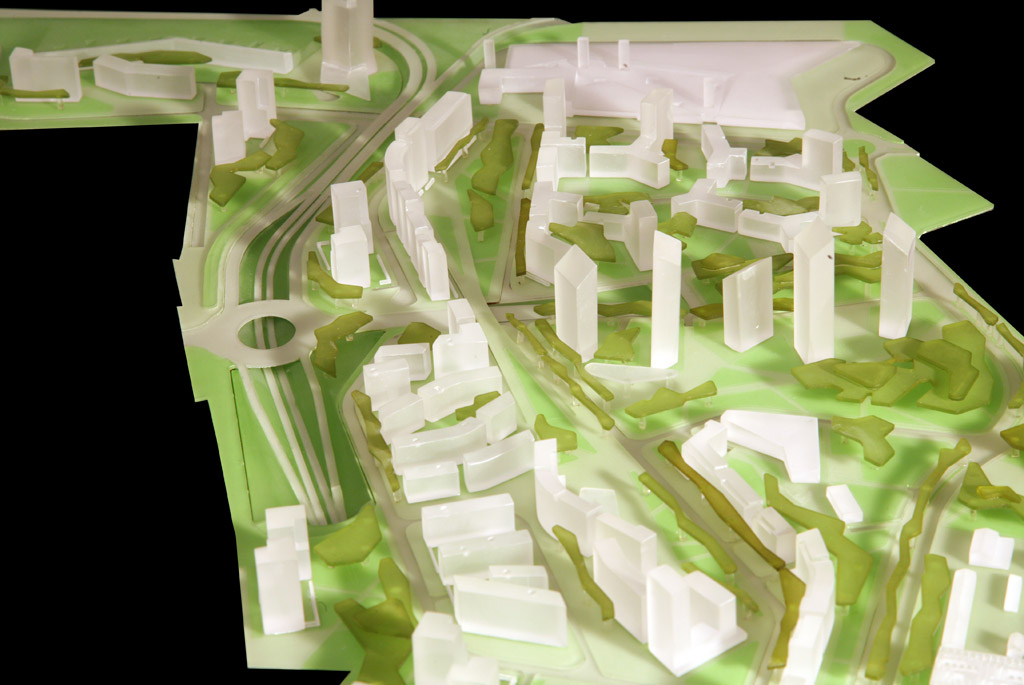
Creation of models for architecture, urban planning, competitions and promotional purposes

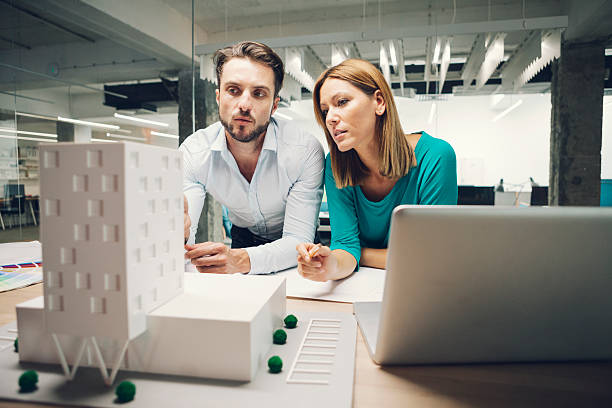
Creating architectural models for various purposes, such as architecture, urban planning, competitions, and promotion, is an essential part of the design process. These models serve as a communication tool that helps architects, clients, and stakeholders visualize and understand the design, scope, and impact of a project. Here is a guide to creating models for different purposes:
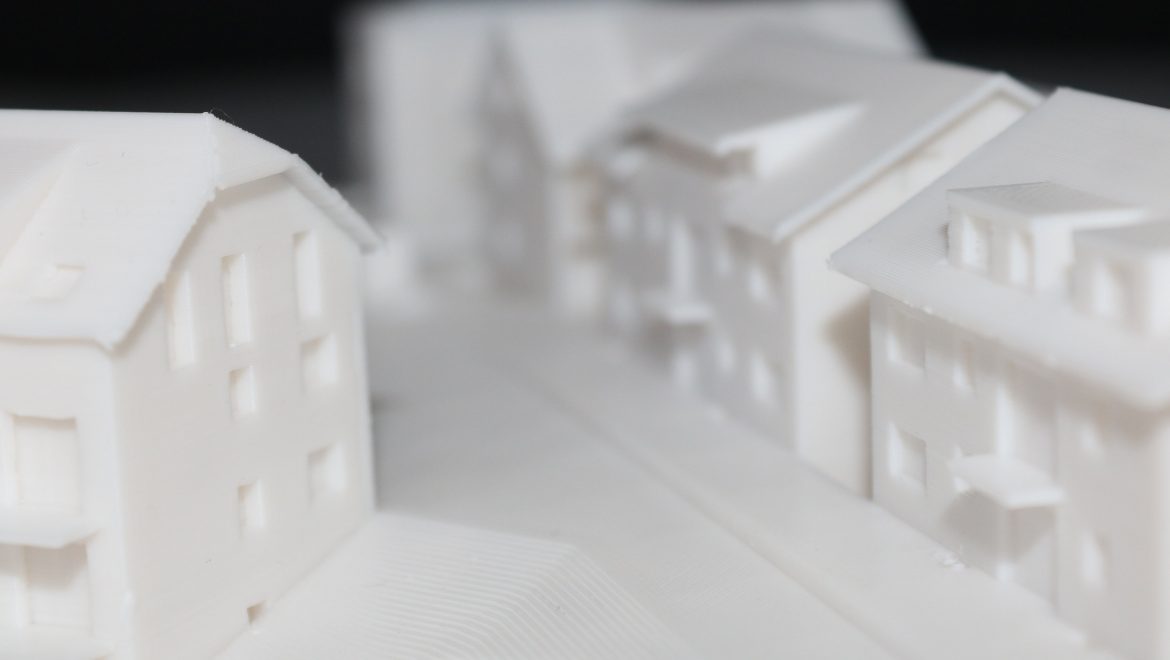
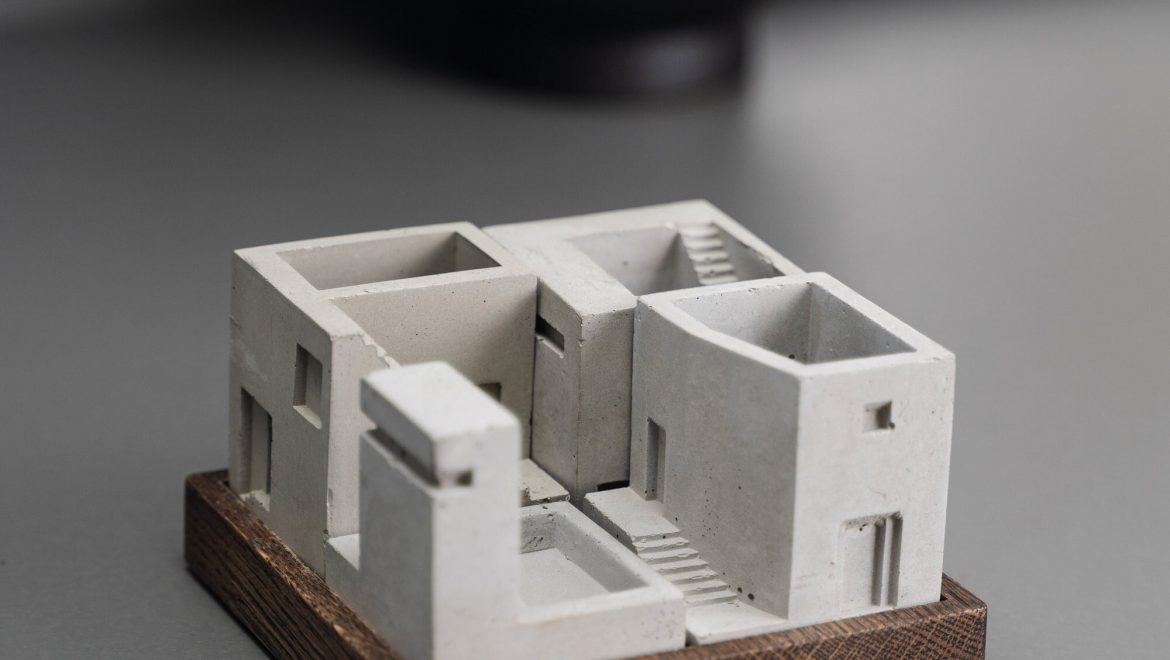
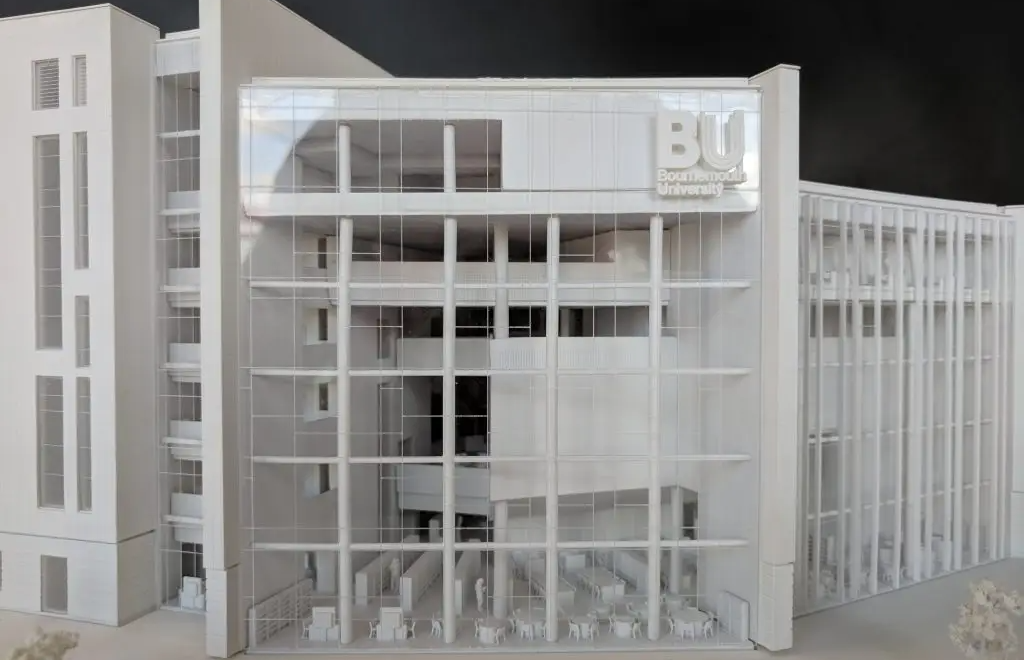
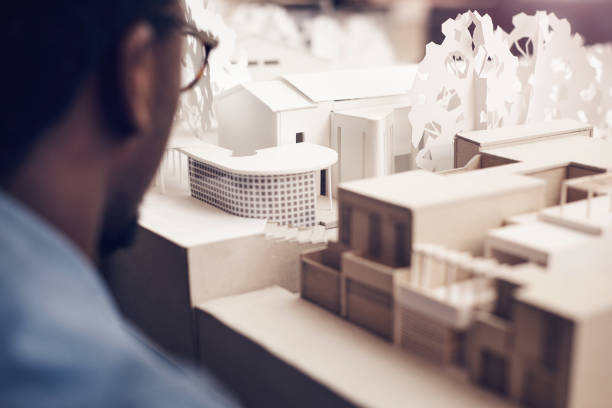
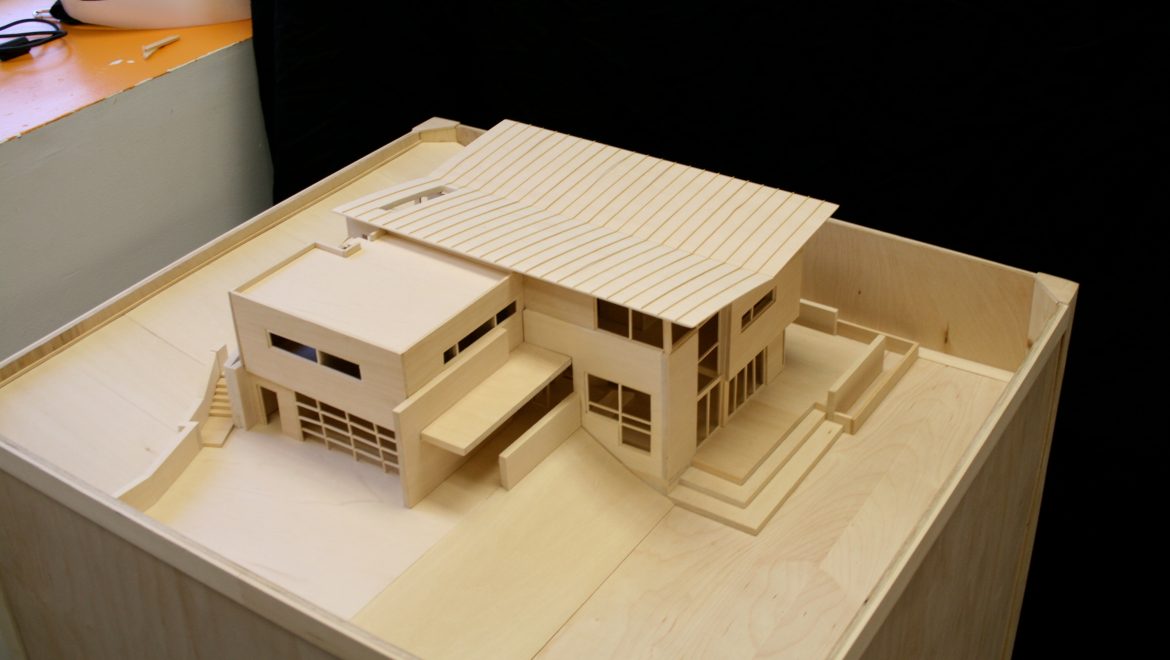
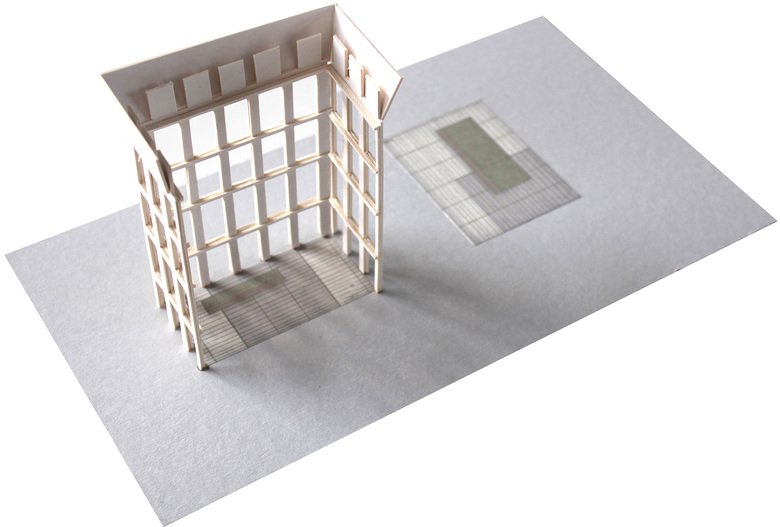
Architectural models: These models represent specific buildings or structures, showcasing design elements such as the form, materials, and spatial relationships. They can range from simple massing models to highly detailed representations with interior and exterior elements.
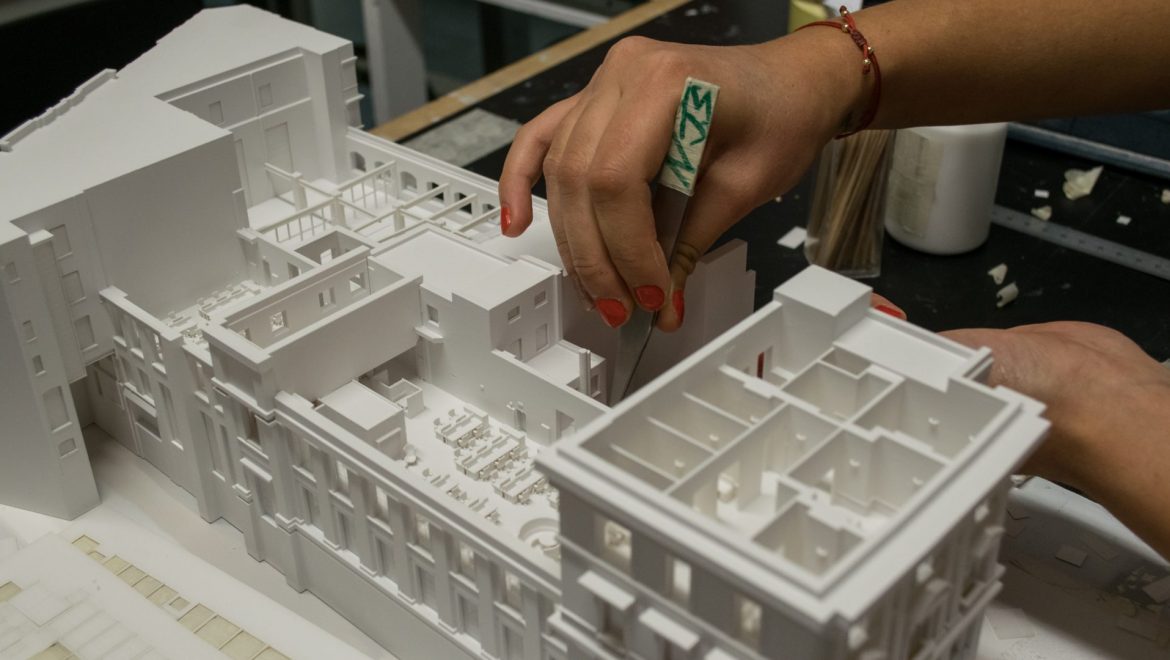
Choose the scale and materials: Determine the appropriate scale for your model, considering the size of the building and the level of detail you want to achieve. Select materials that best represent your design, such as foam, wood, acrylic, or 3D printed components.
Create a base: Prepare a sturdy base for your model, using materials like plywood, MDF, or foam core. The base should provide context for your design, such as the surrounding landscape or urban environment.
Assemble the model: Construct the model based on your design drawings, starting with the main structural elements and gradually adding details and finishes.
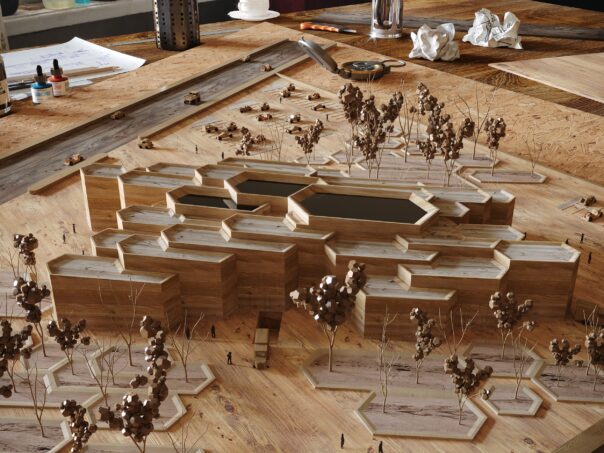
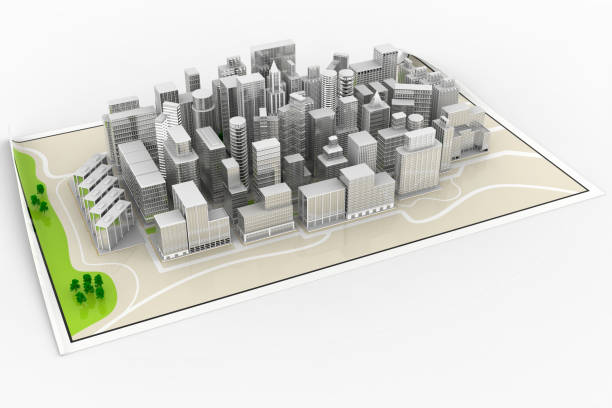
Urban planning models: These models focus on the layout and organization of urban environments, illustrating the relationship between different buildings, public spaces, and infrastructure.
Determine the scope and scale: Define the area you want to represent and select an appropriate scale that allows for a clear understanding of the urban context.
Include key elements: Incorporate important components of the urban environment, such as streets, parks, public transportation, and landmarks.
Show the interaction between built and natural environments: Highlight how the proposed design interacts with the surrounding landscape, water bodies, and green spaces.
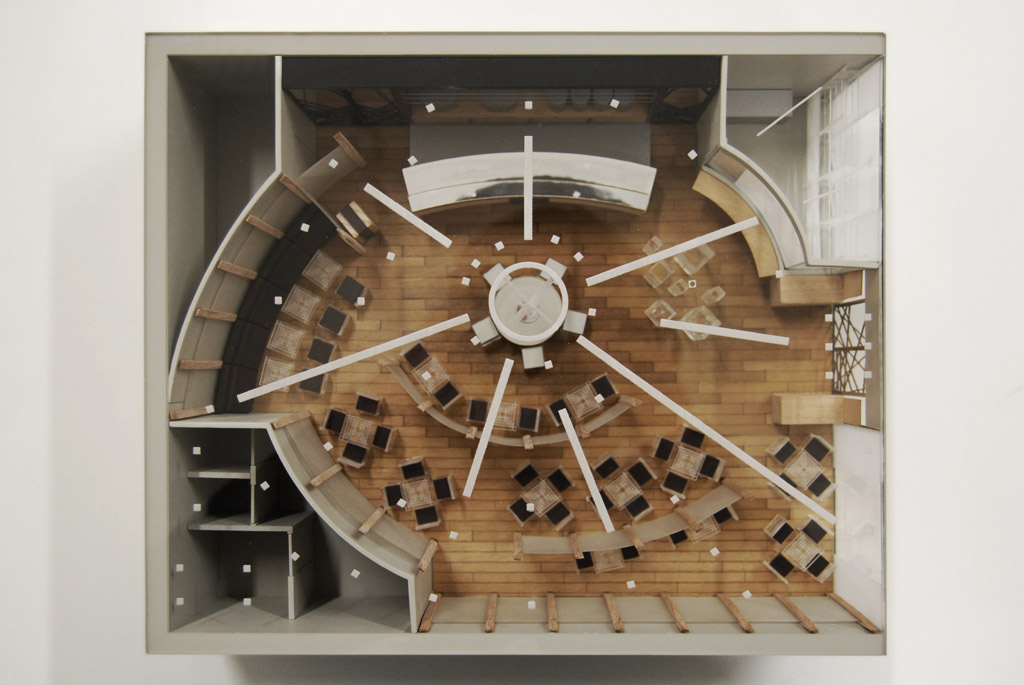
Competition models: When participating in an architectural competition, your model should effectively communicate your design concept and stand out from other entries.
Emphasize the design concept: Focus on the key aspects of your design that make it unique and innovative.

Use high-quality materials and finishes: Invest in high-quality materials and craftsmanship to create a polished and professional-looking model.
Include explanatory materials: Provide diagrams, renderings, or written descriptions to support and explain your design concept.
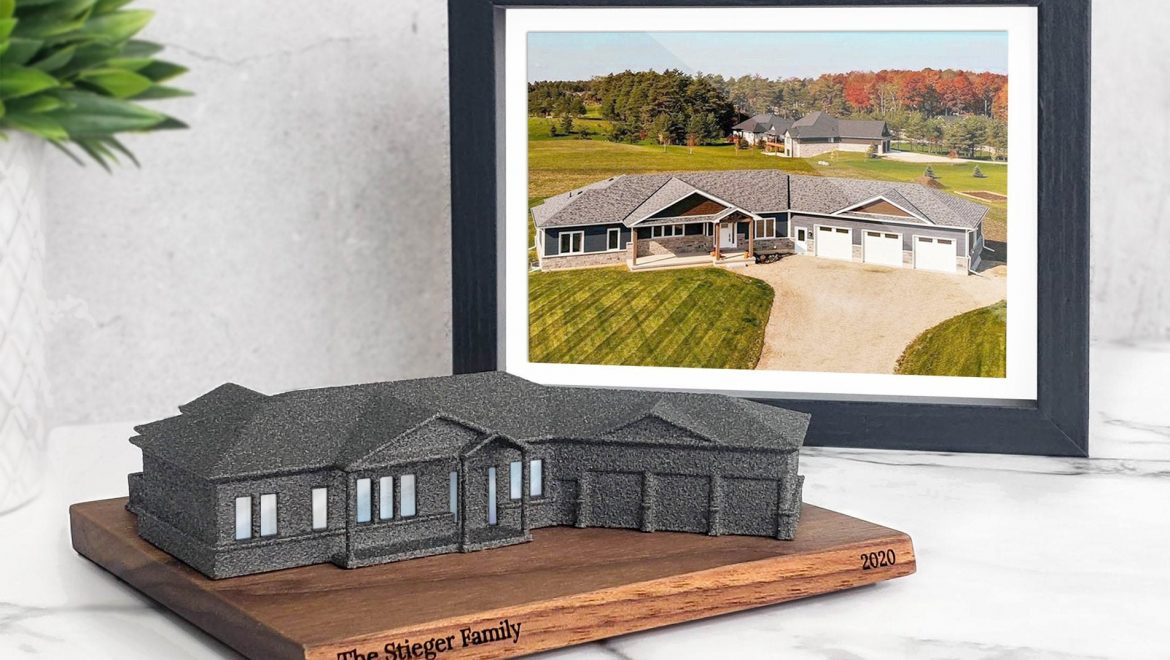
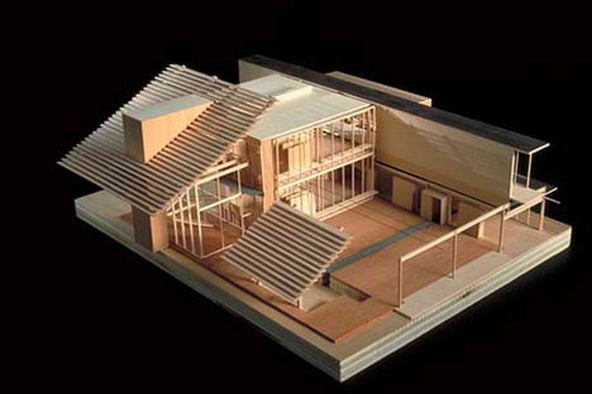
Promotional models: These models are intended to generate interest and excitement around a project, often used for marketing, sales, or fundraising purposes.
Create a visually appealing model: Use eye-catching materials and finishes to make your model stand out and attract attention.
Highlight key features: Showcase the most attractive and unique aspects of your design to pique the interest of potential clients, investors, or buyers.
Consider the presentation: Display your model in a well-lit, professional setting, such as a sales office, exhibition, or event.
By understanding the specific purpose and audience of your architectural model, you can tailor the design, materials, and presentation to effectively communicate your vision and achieve your objectives.